Are Korean and Japanese cultures similar? Exploring the differences between Japan and South Korea
This question could belong to a university dissertation or be a researchers’ life long subject! But in this blog, we will focus on some key differences and similarities, which may be useful to know when doing business in this region of East Asia.
Are Japan and Korea the same?
With only a few hundred kilometres between them, it may be assumed that there is little difference between life in Japan and South Korea. But these two distinct countries each have their own histories, cultures, languages and traditions.
Japan is an island nation. Its four main islands are Honshu, Hokkaido, Kyushu and Shikoku, but it also has numerous smaller islands. The capital city is Tokyo and the official language is Japanese. Japan has a rich cultural heritage, including traditions such as tea ceremonies, kimono wearing and various forms of martial arts.
The Korean Peninsula is divided into two separate countries: North Korea (officially the Democratic People's Republic of Korea) and South Korea (officially the Republic of Korea). The capital of South Korea is Seoul, while the capital of North Korea is Pyongyang. Korean culture is characterised by its unique cuisine, music, dance and art. The Korean language is spoken in both North and South Korea. At present, North Korea remains largely closed to foreign businesses, so we will focus on South Korea.
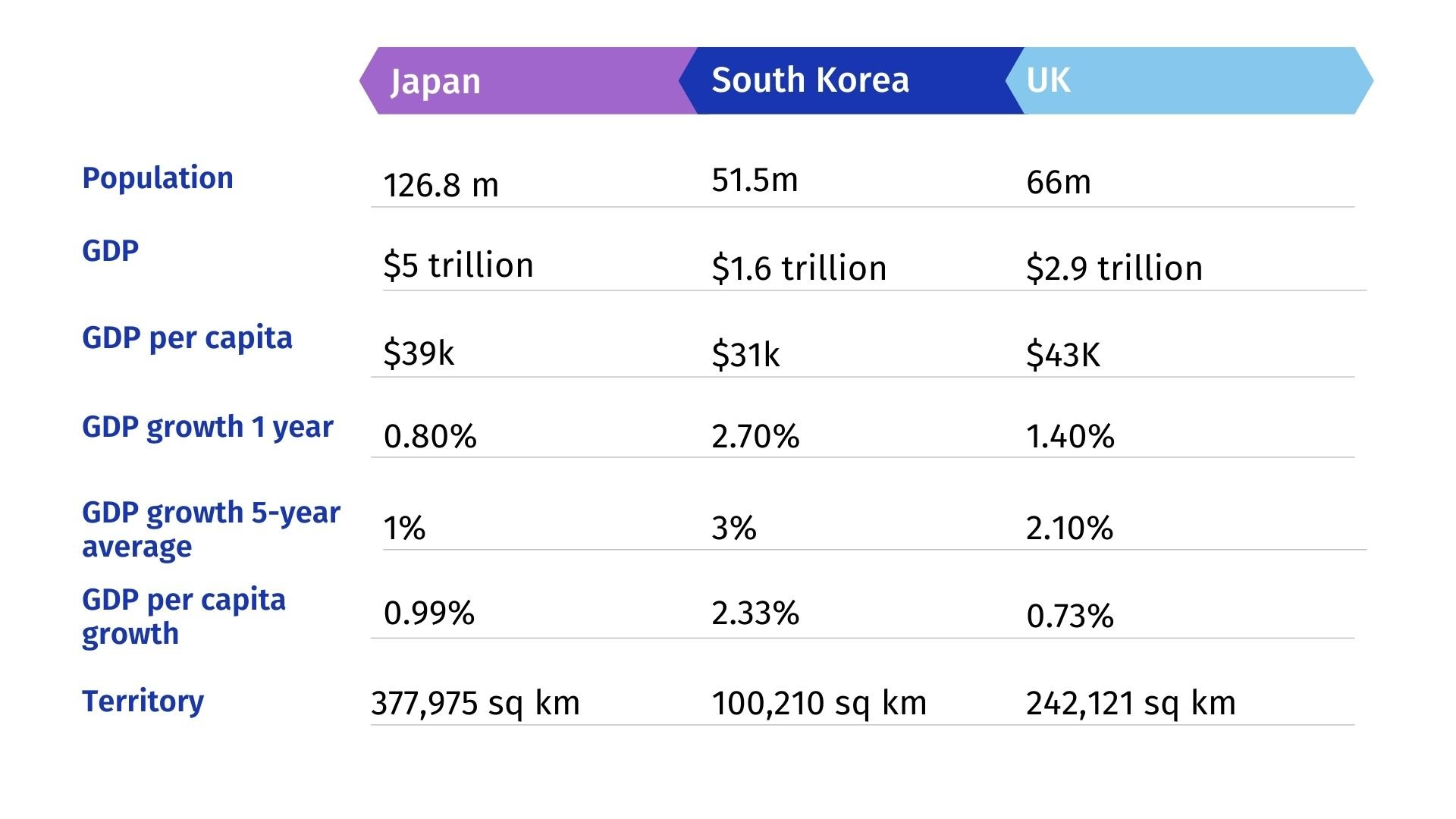
While Japan and the Korean nations share some cultural influences due to their geographical proximity and historical interactions, they have distinct identities and are separate sovereign nations. Having an idea of the difference in scale is a useful place to start.
Japan vs South Korea Economies: 61 Stats Compared (georank.org)
What’s the difference between Japan and South Korea in a business setting?
Differences between Japan and South Korea can be observed in various aspects of business culture, management style, corporate structures and economic focuses.
Business Culture
Japan tends to have a more hierarchical and formal business culture than that of South Korea. Respect for authority and seniority is highly valued in Japanese business settings, with formalities strictly followed. Korean business culture also emphasises hierarchy, but may be less formal than Japan. Nevertheless, respect for seniors and maintaining harmony within the organisation are important aspects of both business cultures.
Management Styles
Japanese management is often characterised by consensus-building, long-term planning and a focus on maintaining relationships with stakeholders, such as employees, suppliers and customers. In practice this means it can take time to reach decisions and change may be incremental.
Korean management styles often emphasise decisiveness, innovation and rapid decision-making. South Korean companies are known for their agility and ability to adapt quickly to changing market conditions.
Corporate Structures
Japanese corporations often have complex and multi-layered organisational structures. Lifetime employment is a traditional practice in many Japanese companies, although this has begun to change in recent years.
South Korean corporations tend to have more streamlined organisational structures with a focus on efficiency and performance. Employment practices are also less focused on lifetime employment.
Economic Focuses
Japan has traditionally been known for its strong manufacturing sector, with companies like Toyota, Sony and Panasonic leading the way in automotive, electronics and other industries.
South Korea has seen rapid growth in sectors such as technology, electronics, automotive, shipbuilding and entertainment. Companies like Samsung, LG, Hyundai and Kia have become global leaders in their respective industries.
Globalisation
Japanese companies have a long history of international expansion and global partnerships. However, they may sometimes face challenges in adapting to new business environments due to their adherence to traditional Japanese business practices.
South Korean companies have also been expanding globally, with a focus on innovation and competitiveness. They may be more adaptable to different business environments and more willing to take risks than Japanese companies.
Of course, these observations are generalisations and there are exceptions within each country. However, understanding these differences is crucial for businesses looking to engage in trade, investment or partnerships with Japanese and South Korean counterparts.
What are the differences between Japan and Korean cultures?
The cultures of Japan and South Korea are rich and distinctive, each stemming from their unique histories, traditions and social behavioural customs. Here are some key cultural aspects to consider.
Language
Japanese and Korean are distinct languages with different linguistic roots, writing systems and phonologies. Both languages have borrowed words from each other over time, reflecting the interaction between the nations over time and the resulting shared heritage. However the two languages remain distinct and speakers of one would not understand the other, unless specifically studied.
Social Etiquette
Japanese culture places a strong emphasis on politeness, respect for hierarchy and maintaining harmony in social interactions. Bowing is a common form of greeting and there are various levels of honorific language used, based on the social status and relationship between individuals.
Korean culture also values politeness and respect, but it may be somewhat less formal than Japan. In South Korea, age and seniority play significant roles in social interactions and there are specific honorifics and speech styles used to address elders and superiors.
Cuisine
Japanese cuisine is known for its emphasis on fresh, seasonal ingredients and aesthetic presentation. Staples of Japanese cuisine include sushi, sashimi, tempura and ramen.
South Korean cuisine is characterised by its bold flavours, use of fermented ingredients and communal dining culture. Kimchi, bulgogi, bibimbap and Korean barbecue are popular dishes.
Arts and Entertainment
Japanese traditional arts such as the tea ceremony, ikebana (flower arranging), calligraphy and traditional theatre forms like Noh and Kabuki, are highly regarded and have a long history.
Korean traditional arts include pottery, painting, and traditional music such as pansori (narrative singing) and samulnori (percussion music). In recent years, South Korean popular culture, including K-pop, dramas and movies, has gained immense attention and new fans worldwide.
Religion
Japan has a diverse religious landscape, with Shintoism and Buddhism being the two major religions. Shintoism involves the worship of kami (spirits or gods) and is deeply intertwined with Japanese culture and traditions.
Korea has been influenced by Buddhism, Confucianism and shamanism. Confucian values such as filial piety and respect for elders have historically played a significant role in Korean society. However, Protestantism is now the most popular religion in the country.
Fashion and Beauty
Japanese fashion is often characterised by its avant-garde and eclectic styles, with a focus on creativity and self-expression. However, traditional Japanese clothing such as the kimono, is still worn for special occasions.
South Korean fashion tends to be more trend-focused and influenced by streetwear and K-pop culture. South Korea is also known for its beauty industry, with its skincare and cosmetics products gaining popularity worldwide.
These are just a few examples of the cultural differences between Japan and South Korea. Each has made a significant contribution to global culture and society and this is set to continue.
K-pop Vs. J-pop
K-pop and J-pop started to grow in the 1980s but have taken different paths. At the moment, there is great international interest in K-pop. These popular youth cultures are a good example to illustrate some subtle but clear difference between the two national cultures.
J-pop encompasses a wide range of genres including pop, rock and R&B, with lyrics primarily in Japanese. Given Japan's karaoke culture, popular songs feature traditional melodies and chords that are simple and easy for the average person to sing.
In contrast, K-pop, while based in the Korean language, also incorporates a lot of English lyrics. With less emphasis on karaoke in South Korea, K-pop tends to feature strong beats and danceable tunes, often with more complex compositions.
K-pop idols are known for their sexy and stylish appearance, especially female idols. On the other hand, J-pop idols often aim for a more innocent and approachable look, with emphasis placed on developing relatable personalities.
While it's true that South Korean nationals dominate K-pop and Japanese nationals dominate J-pop, there are exceptions. There are numerous Japanese K-pop idols and Korean idol groups active in Japan. K-pop enjoys immense popularity in Japan, evident from the success of Japanese K-pop stores nationwide. Many Japanese women aspire to emulate K-pop idols, contributing to the popularity of South Korean cosmetics and Korean-style makeup in Japan.
The triumph of K-pop culture has been backed by the South Korean government. It has recognised Korean Wave (Hanllyu) as an important export industry and promoted it through subsidies, tax incentives, development and promotion programs. The South Korean business culture also helped, allowing quick decision making, mobilisation of the industry and the creative freedom to contribute to the explosion of this popular culture worldwide.
You can read more about South Korea’s cultural exports here:
Ask, don’t assume!
Even if at first glance there may be similarities, it is always important to treat cultures and nations as separate entities. Do your research before starting to do business in a new territory and make no assumptions based on your own culture or knowledge of other countries in the region.
Pointblank Promotions can provide tailored support to companies wishing to expand into the Japanese market. Please feel free to contact us to discuss your needs using the enquiries link below.
Contact us : Pointblank Promotions Ltd
This article was created in partnership with ChatGPT and humans from Pointblank